Understanding Leaf Mold
A Precious Soil Amendment
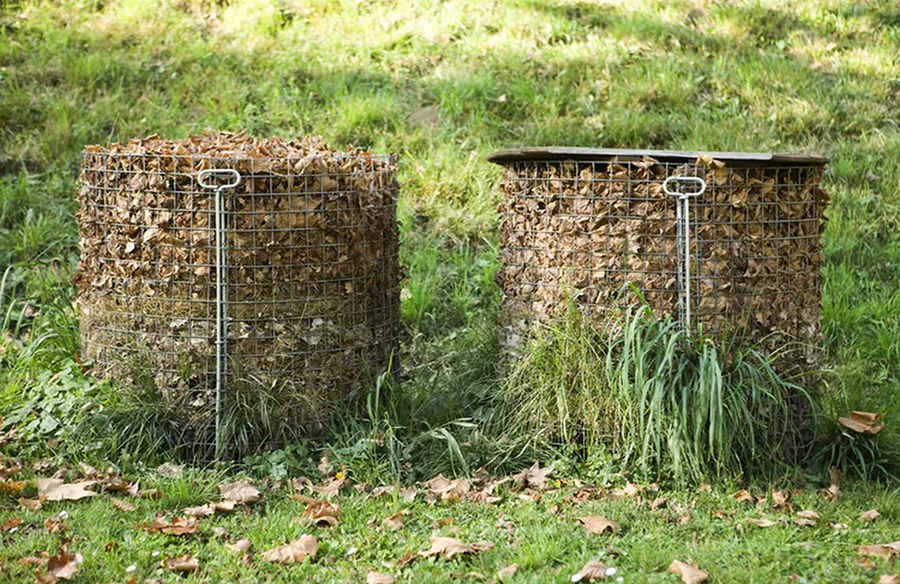
Leaf mold, a product of decomposed leaves, serves as a valuable soil conditioner and mulch in garden beds. Unlike traditional compost, leaf mold is solely composed of leaves and undergoes decomposition primarily through fungal activity, distinguishing it from bacterial-driven composting processes.
Utilizing Leaf Mold as Soil Enhancement
Incorporating homemade leaf mold enriches soil structure and fertility, promoting optimal plant growth. Following a year-long decomposition process, the resulting crumbly material serves as an excellent mulch for trees and shrubs. Over time, it progressively breaks down, nourishing the soil beneath and fostering a thriving ecosystem of soil organisms.
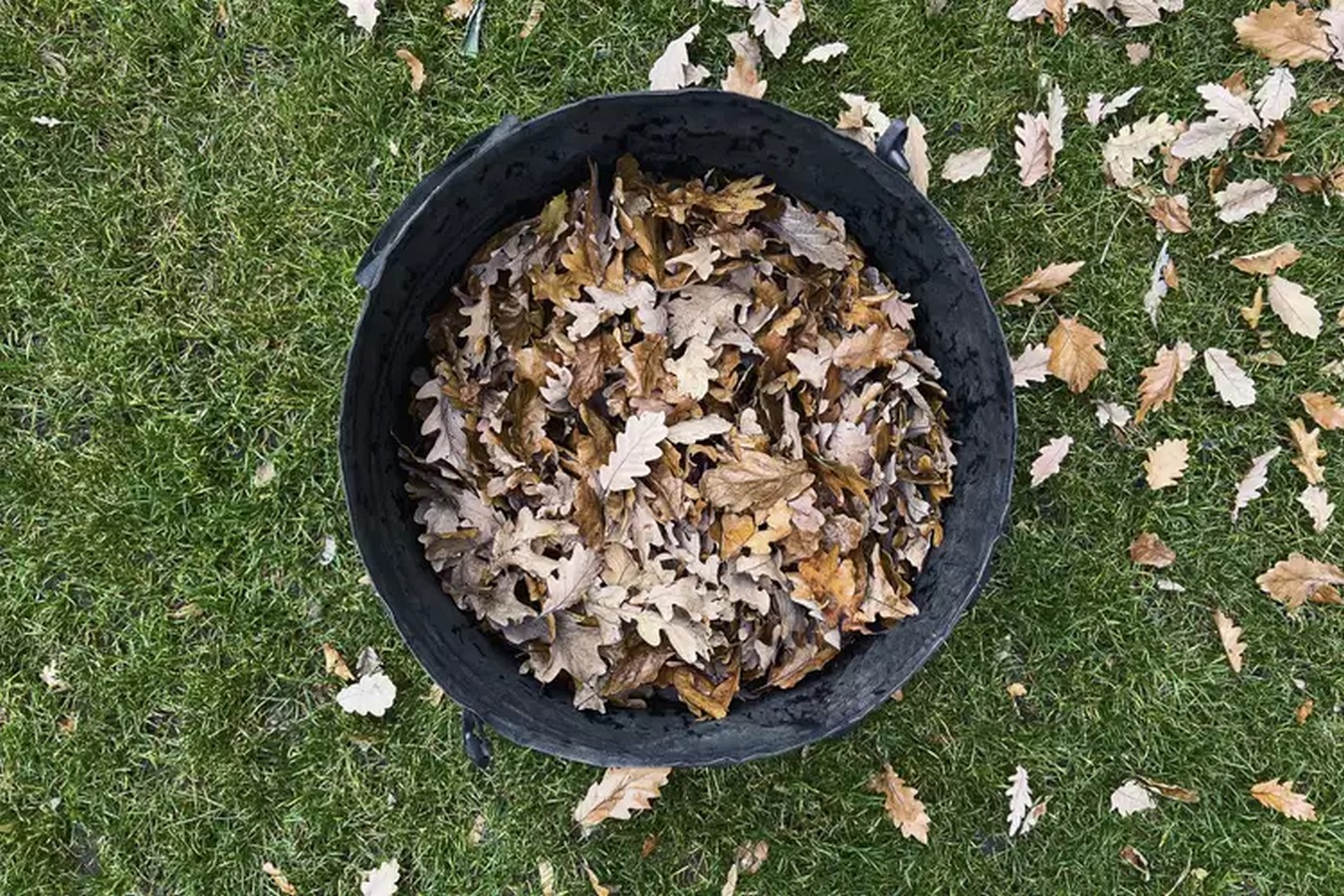

The Versatility of Leaf Mold
Elevating Planting Beds
Leaf mold finds utility in various gardening techniques, including lasagna gardening and sheet mulching. As an upper layer in these methods, it provides a conducive environment for planting while gradually improving soil health. Furthermore, its application minimizes soil disturbance, contributing to the preservation of soil structure and biodiversity.
Enhancing Potting Mixes
In homemade potting mixes, leaf mold plays a pivotal role in moisture retention and aeration. By substituting vermiculite with leaf mold, gardeners achieve a sustainable solution that balances water retention and air circulation within containers. This blend, comprising loamy soil, homemade compost, and leaf mold, fosters optimal conditions for seed germination and plant growth.
Practical Applications and Benefits
Promoting Sustainable Gardening Practices
The integration of leaf mold into gardening practices aligns with principles of sustainability and ecosystem preservation. By repurposing organic materials from the garden, such as spent potting mixes, gardeners contribute to the cyclical regeneration of soil nutrients and structure. Moreover, the use of leaf mold mitigates the reliance on synthetic soil additives, fostering self-sufficiency and environmental stewardship.

Observing Positive Soil Health Indicators
Anecdotal evidence suggests that the application of leaf mold correlates with improved soil health indicators, such as increased earthworm activity and soil aeration. These observations underscore the symbiotic relationship between organic matter supplementation and soil vitality, reinforcing the importance of integrating leaf mold into garden management practices.
Conclusion: Embracing Leaf Mold for Garden Success
Embrace the Potential of Leaf Mold
As an invaluable resource freely available in the garden, leaf mold embodies the essence of sustainable gardening. By harnessing its inherent benefits, gardeners can cultivate vibrant ecosystems, foster plant resilience, and promote soil regeneration. From enriching garden beds to enhancing potting mixes, leaf mold serves as a testament to the transformative power of organic materials in cultivating thriving landscapes.